What causes Bronchial Irritation?
Bronchial irritation is a common respiratory issue that can disrupt your daily life and cause discomfort. It is commonly linked to bronchitis1, an inflammation of the lining of your bronchial tubes, which can be an acute or chronic condition. Whether you're experiencing bronchial irritation or looking to prevent this condition, understanding its origins and management is essential for better respiratory health. Learn what causes bronchial irritation, common symptoms, and how to treat it.
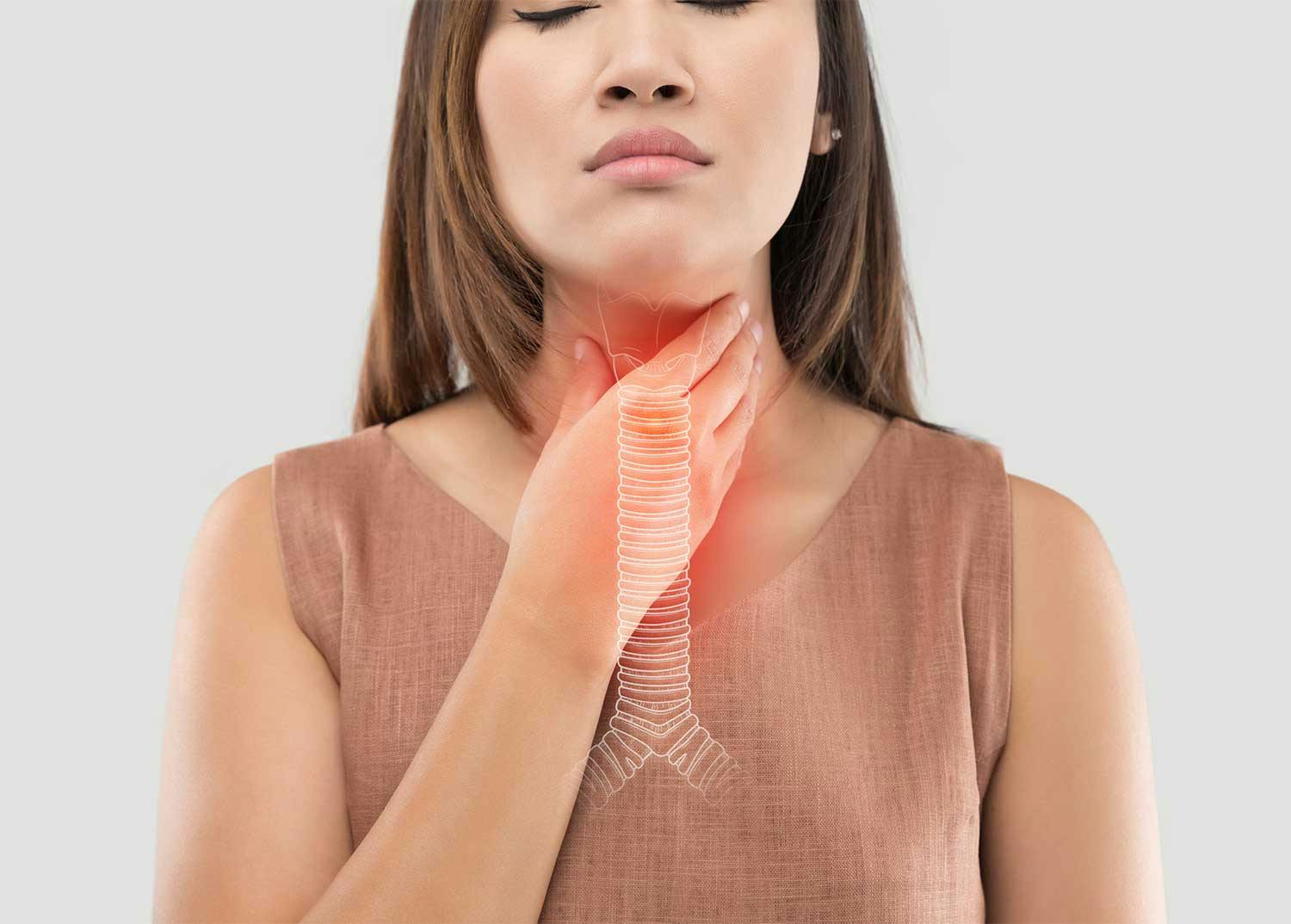
What Is Bronchial Irritation?
Bronchial irritation, or bronchitis1, refers to the inflammation of the bronchial tubes—the airways responsible for carrying air to and from your lungs. When these bronchioles become irritated, it can lead to various respiratory symptoms, making it challenging to breathe comfortably2.
Bronchial irritation can manifest as acute bronchitis or chronic bronchitis, both of which are characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes.1 Acute bronchitis is usually temporary and often caused by viral infections, with a recovery time of a few days to weeks.2Chronic bronchitis is a more persistent condition that is defined as lasting for at least three months and returning for at least two years in a row.2Risk factors for chronic bronchitis include smoking, family history of COPD, older age, history of respiratory disease, exposure to fumes or certain dusts, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).2
Common Symptoms of Bronchial Irritation
Bronchial irritation has several symptoms that affect your wellbeing. Common symptoms include:1
- Coughing: Persistent coughing is a hallmark symptom of bronchial irritation.
- Mucus production: An increase in mucus production is common, which can be clear, white, yellowish-gray or green in color.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath is another frequent symptom.
- Chest discomfort: You may experience chest discomfort or tightness with inflammation of the bronchial tubes.
- Fatigue: Chronic bronchial irritation can leave you feeling fatigued while you manage the strain on your bronchial tubes.
What contributes to bronchial irritation?
Understanding the causes of bronchial irritation, and acute bronchitis, is crucial for prevention and effective management. Several factors can contribute to this condition:3
- Viral infections: Acute bronchial irritation is often triggered by viral infections such as the rhinovirus (the common cold), influenza, coronavirus, and other viral infections.
- Bacterial infections: In some cases, bacterial infections can lead to bronchial irritation. Bacteria that can cause bronchitis include whooping cough and pneumonia. Talk with your doctor for treatment if you are diagnosed with either of these bacterial infections.
- Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for chronic bronchial irritation. The chemicals in cigarette smoke can irritate and damage the bronchial tubes over time, and lead to chronic bronchitis.2
- Pollution and environmental factors: Exposure to environmental irritants like air pollution, dust, and chemicals can contribute to bronchitis, or bronchial irritation. Be cautious if you work in an industry with high exposure to irritants.
Treatment and prevention
Effectively managing bronchial irritation is essential for improving respiratory health and reducing discomfort. The treatment approach may vary depending on the underlying cause:
- Prescription medications: In cases of severe or chronic bronchial irritation or chronic bronchitis, prescription medications may be necessary. If you have allergies, asthma, or COPD, your doctor may recommend an inhaler or other medications. They may also recommend antibiotics for bacterial infections. Consult with your medical provider if you need relief.
- Smoking cessation: If smoking is the underlying cause of bronchial irritation, quitting smoking is crucial for long-term improvement. 4
- Avoiding irritants: Preventing exposure to environmental irritants such as air pollution, paint, household cleaners, or workplace chemicals is essential for reducing the risk of bronchial irritation. Wear a mask in hazardous environments to reduce exposure. 4
- Use a humidifier: Humidifiers can help alleviate coughs and loosen mucus in your airway by providing warm and moist air. 4
Bronchial irritation, often associated with bronchitis, can be caused by various factors, including viral and bacterial infections, smoking, and environmental irritants. Recognizing the symptoms and addressing the underlying causes are key to effective management. By understanding the causes and seeking appropriate treatment, you can find OTC relief or consult with your medical provider to improve your respiratory health and enjoy a more comfortable life. For other ways to find relief from congestion, cough, colds, and more, visit our Cough and Cold Center.
Source Citations:
- Bronchitis: Symptoms and Causes. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bronchitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20355566 Accessed 11/03/2023.
- Bronchitis. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/bronchitis. Accessed 11/03/2023.
- Bronchitis. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/3993-bronchitis. Accessed 11/03/2023
- Bronchitis: Diagnosis and Treatment. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bronchitis/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20355572 . Accessed 11/03/2023.